Pregnancy and Embryonic Development
Pregnancy and Embryonic Development: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Pregnancy, Placenta, Stem Cells, Embryonic Development, Human Placental Lactogen, Gastrulation, Relaxin, Human Chorionic Gonadotropin and, Progestogens
Important Questions on Pregnancy and Embryonic Development
The embryonic structure that gets implanted in the uterine wall of a human female is
Placenta is connected to the embryo via:
Which of the following are the types of stem cells?
Human placental lactogen is secreted during pregnancy by syncytiotrophoblast and increases lipolysis.
A hormone secreted from the placenta and increases blood glucose level of a pregnant woman is known as _____. (Human placental lactogen/Human chorionic gonadotropin)
Select the one that has anti-insulin properties, a polypeptide hormone secreted during pregnancy, and aids in the energy supply to the foetus:
The amnion of the mammalian embryo is derived from ectoderm and mesoderm.
The types of eggs of placental mammals are Acelithal.
In a human female, the _____ gets implanted to the endometrium by the trophoblast cells.
The first movements of the foetus and the appearance of hair on the head are usually observed during the fifth or second month. Mention it.
Identify the correct statement/s.
The extraembryonic membrane in humans prevents desiccation of the embryo inside the uterus is Amnion.
Name the organ which serves as the interface between foetal and maternal circulation.
Name the scientist who gave the rule of embryonic development.
Mention the respiratory-related structure present in the early-stage of human embryo _____ (Lungs/Gills/gill slits/trachea)
Which of the following are the types of stem cells?
Which of the following hormones is not a secretory product of human placenta?
Fill in the blank with the correct word given in the bracket.
The movement of the _____ (foetus/placenta) inside the mother womb's is known as quickening.
Pharyngeal arch is formed and the quantity of amniotic fluid increases around the embryo during the third to sixth week of gestation.
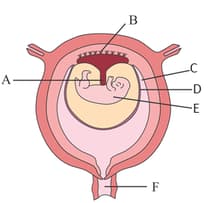
Identify the part marked as 'D' in the above diagram.
